C# Linq中的Select和SelectMany
C#中Linq的select 语句很好理解,因为这个select类似于sql语句中的select——筛选出感兴趣的字段,但是SelectMany就不好理解了,本文主要讲解一下SelectMany,顺便和Select对比。
目录
1.SelectMany的官方定义
官方定义很简单,就是一句话:将一个序列中的每个元素映射成一个可枚举对象,然后将这些对象合并到一个序列中。
看完可能还是有点懵逼,我们再看看函数定义:
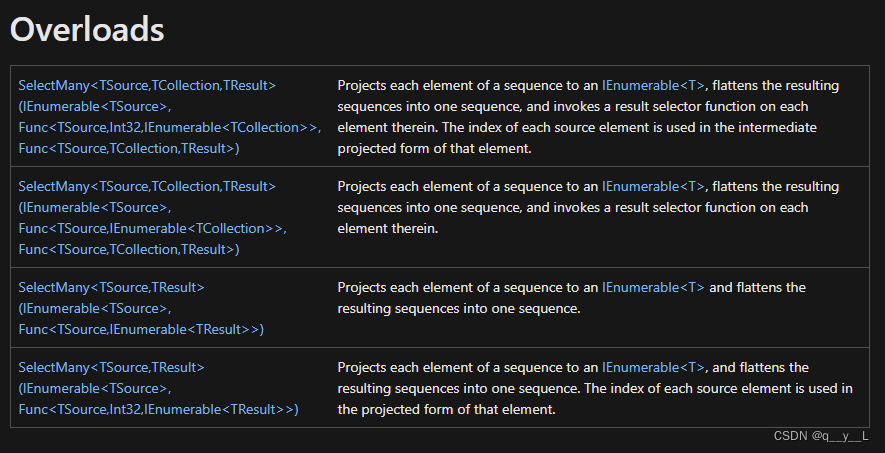
函数定义有点复杂,如果你能看懂,那就不用看下文了。如果觉得理解有点困难就看下面的例子:
2.例子
先看官方的例子:
class PetOwner
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public List<string> Pets { get; set; }
}
public static void SelectManyEx3()
{
PetOwner[] petOwners =
{ new PetOwner { Name="Higa",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Scruffy", "Sam" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Ashkenazi",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Walker", "Sugar" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Price",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Scratches", "Diesel" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Hines",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Dusty" } } };
// Project the pet owner's name and the pet's name.
var query =
petOwners
.SelectMany(petOwner => petOwner.Pets, (petOwner, petName) => new { petOwner, petName })
.Where(ownerAndPet => ownerAndPet.petName.StartsWith("S"))
.Select(ownerAndPet =>
new
{
Owner = ownerAndPet.petOwner.Name,
Pet = ownerAndPet.petName
}
);
// Print the results.
foreach (var obj in query)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
}
// This code produces the following output:
//
// {Owner=Higa, Pet=Scruffy}
// {Owner=Higa, Pet=Sam}
// {Owner=Ashkenazi, Pet=Sugar}
// {Owner=Price, Pet=Scratches}
这里调用的是这个函数:
public static System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource,TCollection,TResult> (this System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource,System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<TCollection>> collectionSelector, Func<TSource,TCollection,TResult> resultSelector);
注意第一个参数:
Func<TSource,System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<TCollection>> collectionSelector
传入的是一个func,func的入参为原集合的元素,对应起来就是PetOwner,返回的是Pets成员,也就是集合,从名字上来说就是指定要flatten的集合,简而言之就是给我把Owner的Pets全部撸到一个集合里面去。
第二个参数:
Func<TSource,TCollection,TResult> resultSelector
就是一个选择器,从TSource和TCollection中选择,构成TResult。
如果只是想获取所有的pets信息;可以用另一个版本:
public static System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource,TResult> (this System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource,System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<TResult>> selector);
// Query using SelectMany().
IEnumerable<string> query1 = petOwners.SelectMany(petOwner => petOwner.Pets);
Console.WriteLine("Using SelectMany():");
// Only one foreach loop is required to iterate
// through the results since it is a
// one-dimensional collection.
foreach (string pet in query1)
{
Console.WriteLine(pet);
}
3. Select和SelectMany的对比
看下面的例子:
public class PhoneNumber
{
public string Number { get; set; }
}
public class Person
{
public IEnumerable<PhoneNumber> PhoneNumbers { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
IEnumerable<Person> people = new List<Person>();
// Select gets a list of lists of phone numbers
IEnumerable<IEnumerable<PhoneNumber>> phoneLists = people.Select(p => p.PhoneNumbers);
// SelectMany flattens it to just a list of phone numbers.
IEnumerable<PhoneNumber> phoneNumbers = people.SelectMany(p => p.PhoneNumbers);
这个例子简单明了:用Select得到的是List<List<>>结构,而SelectMany得到的是List<>,所以官方定义会中有flatten这个词。
所以前面的例子用Select代替就可以写为:
// This code shows how to use Select()
// instead of SelectMany().
IEnumerable<List<String>> query2 =
petOwners.Select(petOwner => petOwner.Pets);
Console.WriteLine("\nUsing Select():");
// Notice that two foreach loops are required to
// iterate through the results
// because the query returns a collection of arrays.
foreach (List<String> petList in query2)
{
foreach (string pet in petList)
{
Console.WriteLine(pet);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
4.SelectMany的扩展
官方还提供了一个能获取索引的版本:
public static System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<TResult> SelectMany<TSource,TResult> (this System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource,int,System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<TResult>> selector);
也就是比上一个版本对一个Int类型参数!
class PetOwner
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public List<string> Pets { get; set; }
}
public static void SelectManyEx2()
{
PetOwner[] petOwners =
{ new PetOwner { Name="Higa, Sidney",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Scruffy", "Sam" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Ashkenazi, Ronen",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Walker", "Sugar" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Price, Vernette",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Scratches", "Diesel" } },
new PetOwner { Name="Hines, Patrick",
Pets = new List<string>{ "Dusty" } } };
// Project the items in the array by appending the index
// of each PetOwner to each pet's name in that petOwner's
// array of pets.
IEnumerable<string> query =
petOwners.SelectMany((petOwner, index) =>
petOwner.Pets.Select(pet => index + pet));
foreach (string pet in query)
{
Console.WriteLine(pet);
}
}
// This code produces the following output:
//
// 0Scruffy
// 0Sam
// 1Walker
// 1Sugar
// 2Scratches
// 2Diesel
// 3Dusty
注意,SelectMany所要选择的集合不一定是原对象中的集合:
List<string> animals = new List<string>() { "cat", "dog", "donkey" };
List<int> number = new List<int>() { 10, 20 };
var mix = number.SelectMany(num => animals, (n, a) => new { n, a });
foreach(var x in mix)
{
Console.WriteLine(x.n+"=="+x.a);
}
这样可以很方便的生成笛卡尔积形式结果:
10==cat
10==dog
10==donkey
20==cat
20==dog
20==donkey
本站大部分文章、数据、图片均来自互联网,一切版权均归源网站或源作者所有。
如果侵犯了您的权益请来信告知我们删除。邮箱:1451803763@qq.com


